Designing a theoretical framework for research
Designing a theoretical framework is a creative and iterative process. It is not merely summarising existing theories, nor is it a tick-box exercise. Instead, it is a practical, intellectual activity that strengthens the academic rigour of a study.
A framework should not be fixed after the study begins; it can be refined or adjusted as the research evolves. Importantly, it is usually composed of two or more philosophies, theories, or models, rather than a single one.
Theoretical frameworks are not only for research, but for practice, teaching and learning.
Steps in designing a theoretical framework
- Identify the research that is in the planning stage.
- Locate the parts of the research plan that could benefit from theoretical, philosophical, or model-based guidance.
- Identify multiple relevant theories, philosophies, and models for each research stage.
- Select the most suitable ones and justify your choice.
- Combine the selected components into a coherent framework.
- Name the framework and describe its key components, strengths, and limitations, using visuals if possible.
- Explain and justify its application within your study, ideally with a visual representation.
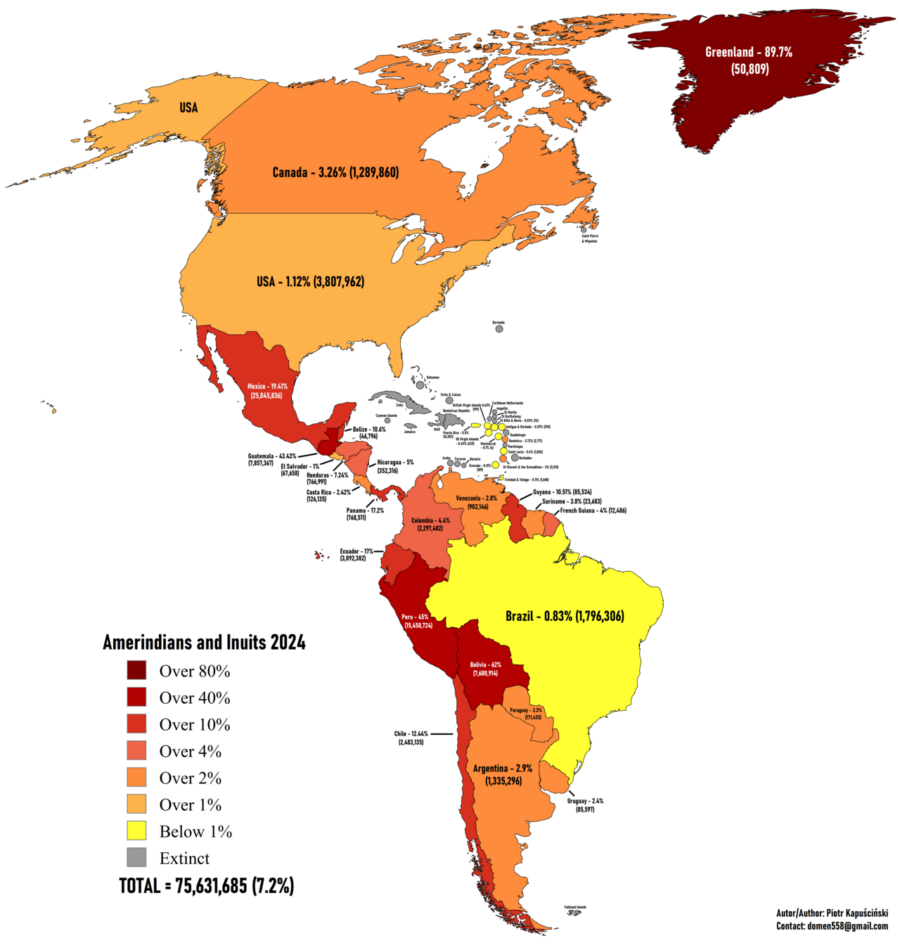
| Part of the Research or Study | Philosophy, Theory or Model | Example (African-based) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Research focus and title | Guided by indigenous African worldviews and relational ontology | Ubuntu Philosophy – emphasises interconnectedness (“I am because we are” (not |
| 2. Research questions or hypothesis | Framed through African ethical and relational perspectives | Africana Womanism – highlights gender, family and communal concerns in question formulation |
| 3. Literature | Informed by African intellectual traditions and decolonial knowledge systems | Afrocentricity (Asante) – recentres African perspectives as legitimate sources of knowledge |
| 4. Positionality | Reflects African epistemology and researcher–community relationship | African Relational Ontology – acknowledges the researcher as part of the community, not detached from it |
| 5. Ethics | Based on African moral philosophy and collective responsibility | Ubuntu Ethics – promotes respect, reciprocity and dignity for participants |
| 6. Research approach | The overall way of knowing and doing research guided by African philosophy | Ubuntu Research Approach (URA) – emphasises harmony, mutual respect and communal participation in the research process |
| 7. Methodology | Framework for conducting research based on indigenous or African ways of knowing | Indigenous Research Methodology (IRM) or Afrikology (Hoppers) – values indigenous epistemologies, participatory processes and community ownership of knowledge |
| 8. Design | Influenced by African participatory and holistic inquiry traditions | Participatory Action Research (Ubuntu-inspired) – encourages collaboration, reflection and empowerment |
| 9. Data collection | Draws on indigenous storytelling, proverbs and communal dialogue | Sankofa Model / African Narrative Inquiry – uses oral histories and storytelling as valid data |
| 10. Analysis | Interprets data through African interpretive and cultural lenses | African Hermeneutics – contextual reading of meaning rooted in culture, symbolism and spirituality |
| 11. Discussion | Links findings to African theoretical thought and local realities | Afrocentric Interpretation – situates findings within African worldviews and collective aspirations |
| 12. Authorship | Guided by communal epistemology and ethics of shared knowledge | Ubuntu Authorship Model – acknowledges community voices and co-creators of knowledge |
Constructing and naming the framework
If your framework combines
Ubuntu Philosophy + Afrocentricity + Indigenous Research Methodology + African Hermeneutics + Ubuntu Ethics,
you might call it:
The Ubuntu–Afrocentric Indigenous Research Framework (UAIRF)
Description – The framework integrates Ubuntu’s communal ethics, Afrocentricity’s cultural centring and Indigenous Research Methodology’s participatory processes. It supports research that is ethically grounded, contextually relevant and intellectually decolonised.
In conclusion
In a research plan, the section on theoretical framework or theories explains how the study will be guided by particular philosophies, theories or models. It justifies their selection, shows their relevance to the research problem and demonstrates how they will shape the study’s design, data collection and analysis. The discussion should identify the key frameworks or theories to be used, outline their origins and major concepts, and explain why they are suitable for the topic. The paragraph should also describe how the different frameworks or theories complement one another and how they will be applied to guide the research process. The tone is forward-looking and written in the present or future tense, for example: “This study will be guided by the Ubuntu–Afrocentric Indigenous Research Framework, which combines Ubuntu ethics, Afrocentric philosophy and Indigenous Research Methodology to ensure cultural relevance and collective engagement.”
In a research report or manuscript, the section on theoretical framework or theories shows how they were actually applied throughout the study. It revisits the guiding frameworks or theories, explains their role in shaping the design, data collection, interpretation and discussion, and reflects on their usefulness and limitations. The researcher should describe how the frameworks influenced the study’s ethical approach, participant engagement and interpretation of results, highlighting any ways in which they were refined during the process. The tone is reflective and analytical, using the past tense, for example: “The study was guided by the Ubuntu–Afrocentric Indigenous Research Framework, which provided a culturally grounded perspective for interpreting participants’ lived experiences and for understanding the communal meanings embedded in the findings.”
Use the form below to subscibe to Owia Bulletin.
Discover more from Africa Social Work & Development Network | Mtandao waKazi zaJamii naMaendeleo waAfrika
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.